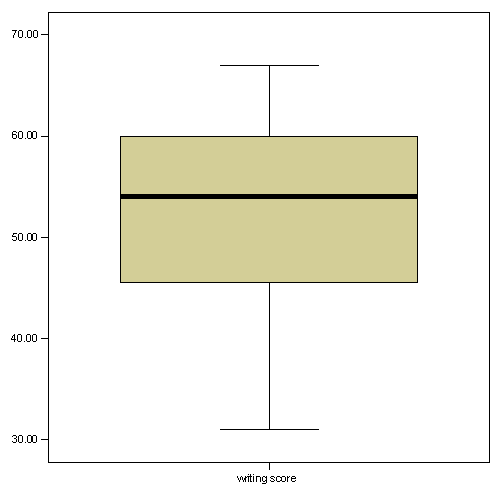Spss Skewness And Kurtosis Interpretation

For skewness if the value is greater than 1 0 the distribution is right skewed.
Spss skewness and kurtosis interpretation. In spss the skewness and kurtosis statistic values should be less than 1 0 to be considered normal. Variables should be normally distributed in the population. Leptokurtic kurtosis 3. But a skewness of exactly zero is quite unlikely for real world data so how can you interpret the skewness number.
Distribution is longer tails are fatter. Because it is the fourth moment kurtosis is always positive. Kurtosis is a measure of whether the distribution is too peaked a very narrow distribution with most of the responses in the center hair et al 2017 p. This lesson is part 2 of 3 in the course basic statistics frm.
Notice how much different the results are when the sample size is small compared to the true skewness and kurtosis for the 5 000 results. You should now be able to calculate statistics for skewness and kurtosis in spss. Skewness is negative the data are negatively skewed or skewed left meaning that the left tail is longer. If the bulk of the data is at the left and the right tail is longer we say that the distribution is skewed right or positively.
If it s unimodal has just one peak like most data sets the next thing you notice is whether it s symmetric or skewed to one side. So observing substantial skewness in some sample data suggests that the normality assumption is violated. Outliers stretch the horizontal axis of the histogram graph which makes the bulk of the data appear in a narrow skinny vertical range thereby giving the skinniness of a leptokurtic distribution. It indicates the extent to which the values of the variable fall above or below the mean and manifests itself as a fat tail.
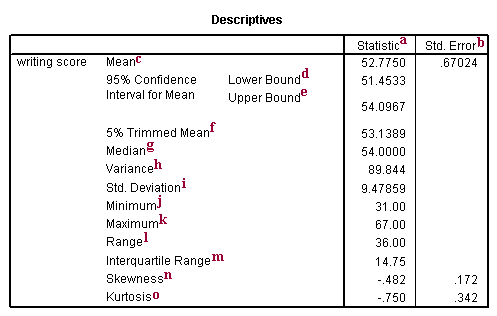
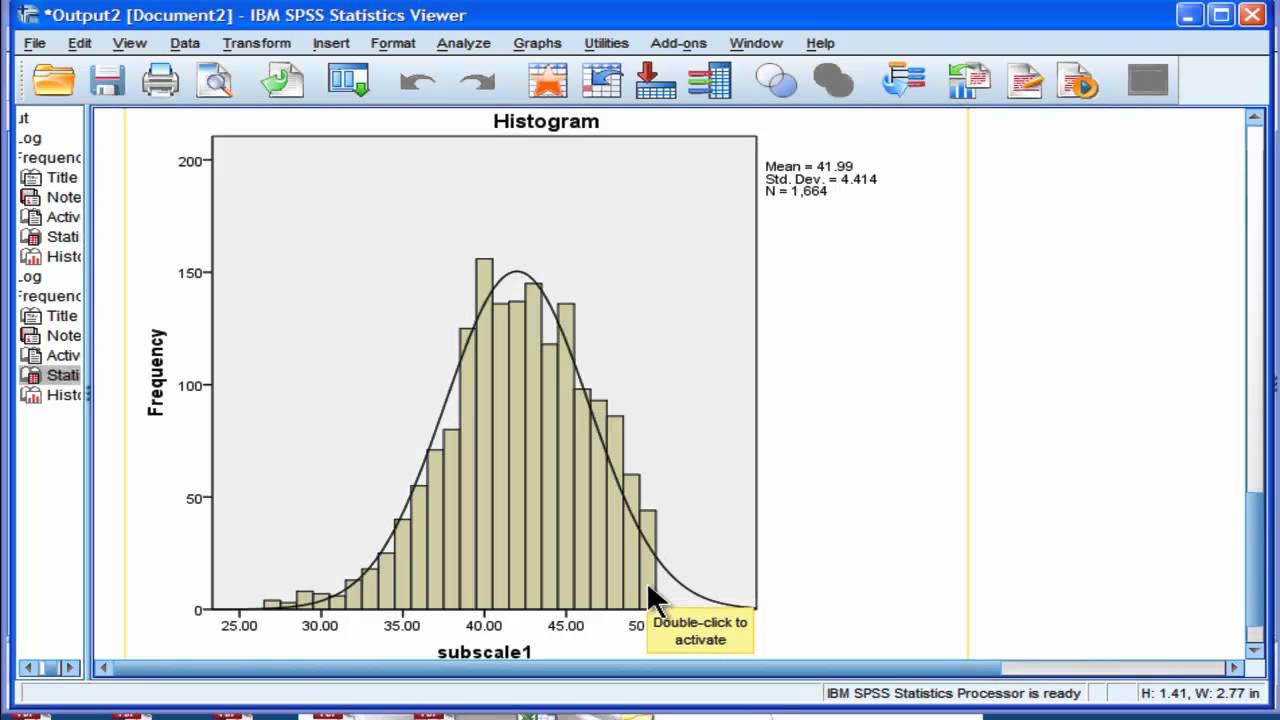
You can also see that spss has calculated the mean 46 93 metres and the standard deviation 21 122 metres. Skewness implications for data analysis. N represents the number of observations. Just like skewness kurtosis is a moment based measure and it is a central standardized moment.
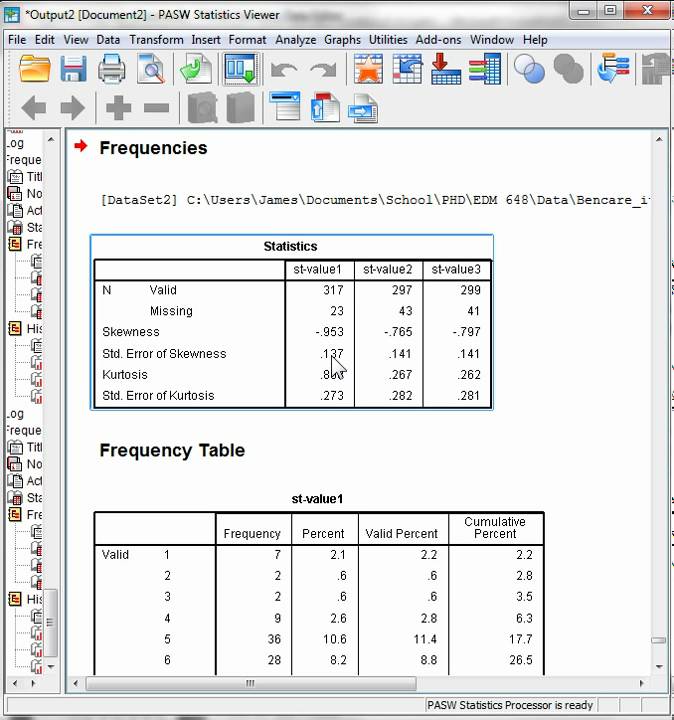
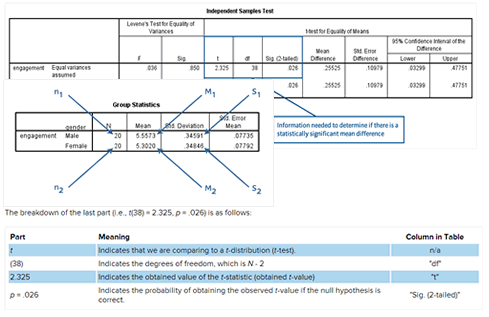
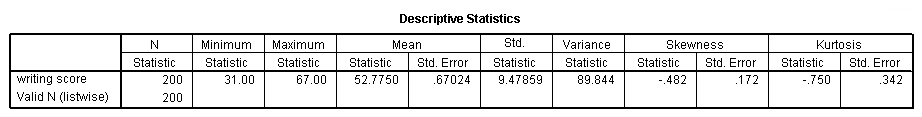
The skewness statistic is 719 and kurtosis is 125 see above. Frm part 1 statistics. When both skewness and kurtosis are zero a situation that researchers are very unlikely to ever encounter the pattern of responses is considered a normal distribution. Kurtosis is sensitive to departures from normality on the tails.
If skewness 0 the data are perfectly symmetrical. For a sample size of 25 the skewness was 356 compared to the true value of 0 007 while the kurtosis was 0 025. Okay that s it for this quick tutorial. The first thing you usually notice about a distribution s shape is whether it has one mode peak or more than one.
Because of the 4th power smaller values of centralized values y i µ in the above equation are greatly de emphasized. G principles of statistics dover. The normal distribution has skewness 0.