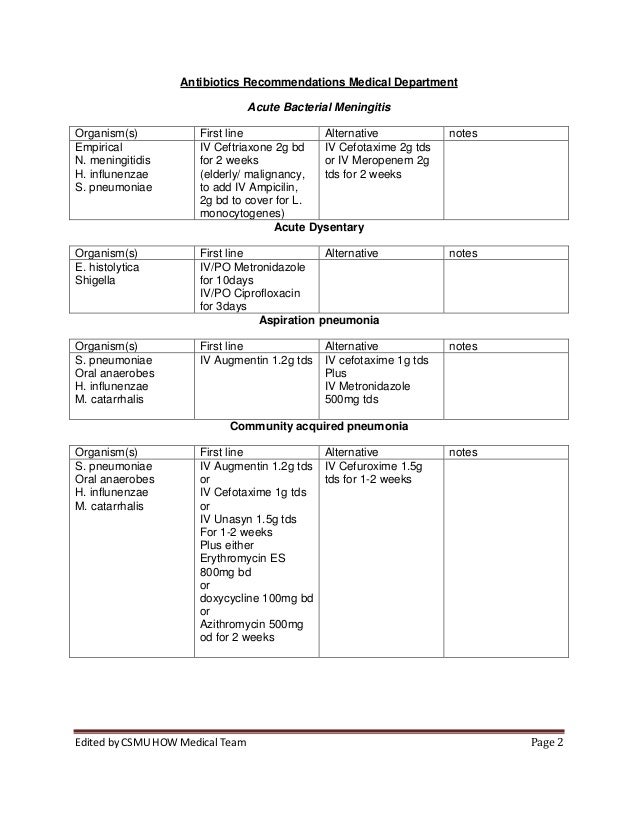
National Antibiotic Guidelines Malaysia

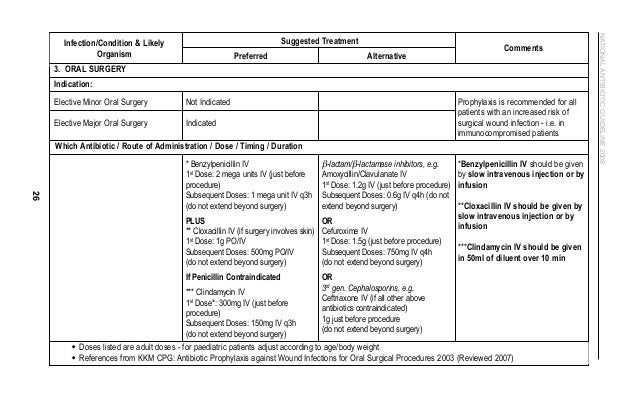
National antibiotic guidelines 2016 respiratory tract infections upper respiratory tract infections urti pharyngitis or tonsillitis exudative or diffuse erythematous associated cough rhinorrhea hoarseness and or oral ulcers suggest a viral etiology the rapid strep test may be used to diagnose group a streptococcus gas pharyngitis.
National antibiotic guidelines malaysia. 1707 malaysia icu antibiotic guidelines 2017 malaysia icu antibiotic guidelines 2017. Rapid identification of patients with infections. National antibiotic guideline second. The threat brought on by antimicrobial resistance.
Unit 1 6 level 1 enterprise 3b technology park malaysia tpm jalan innovasi 1 lebuhraya puchong sungei besi bukit jalil 57000 kuala lumpur malaysia secretariat acadmed my 603 8996 0700 603 8996 1700 603 8996 2700 603 8996 4700. National antimicrobial guideline third edition. This is the 3rd edition of national antimicrobial guideline nag. National antibiotic guideline 2008 malaysia 2008.
The belief that antibiotic use or misuse is a major driving force for antibiotic resistance is now an established and recognised fact. This guideline will hopefully benefit the clinicians pharmacists and all healthcare providers in advocating rationale use of antibiotic and subsequently can curb antimicrobial resistance and minimize healthcare cost. Malaysia icu antibiotic guidelines 2017. Message from the director general of health malaysia the national antimicrobial guideline is one of the most exciting initiatives that ministry of health moh is proud of since its first launch in 2008.
Click on the map image to launch google maps service. Located at jalan pahang 50588 kuala lumpur malaysia. Department of anaesthesiology and intensive care school of medical sciences health campus universiti sains malaysia 16150 kubang kerian kelantan. We operate from 8 00am 5 00pm monday friday.
Refers to activities that help optimise antibiotic therapy ensuring the best clinical outcome for the patient while lowering the risk of development of antimicrobial resistance and minimising adverse effects and costs. Appropriate measures in antibiotic stewardship in icus include.